 |
National Parks
Marine National Parks
National Reserves
- Arawale
- Bisanadi (www)
- Boni
- Buffalo Springs
- Dodori
- Kakamega (www)
- Kamnarok
- Kerio Valley
- Laikipia
- Lake Bogoria
- Losai (www)
- Marsabit (www)
- Masai Mara
- Mwea (www)
- Nasolot
- Ndere Island (www)
- Ngai Ndethya
- North Kitui
- Rahole
- Samburu
- Shaba (www)
- Shimba Hills
- South Kitui
- South Turkana
- Tana River Primate (www)
Marine National Reserves
- Diani
- Kiunga (www)
- Malindi-Watamu (www)
- Mombasa (www)
- Mpunguti
Nature Reserves
- Arabuko Sokoke (www)
- Cheptugen-Kapchemutwa
- Kaimosi Forest
- Kaptagat Forest
- Karura
- Katimok Kabarnet
- Langata
- Mbololo
- Nandi North
- South-Western Mau
- Uaso Narok
Game Sanctuaries
- Kisumu Impala (www)
- Maralai
Wetlands of International Importance (Ramsar)
- Lake Baringo
- Lake Bogoria
- Lake Naivasha
- Lake Nakuru (www)
UNESCO-MAB Biosphere Reserves
- Amboseli National Park (www)
- Kiunga Marine National Reserve (www)
- Malindi-Watamu Biosphere Reserve (www)
- Mount Elgon (www)
- Mount Kenya Biosphere Reserve (www)
- Mount Kulal Biosphere Reserve
World Heritage Convention
- Lake Turkana National Parks
- Lamu Old Town
- Mount Kenya National Park/Natural Forest (www)
|
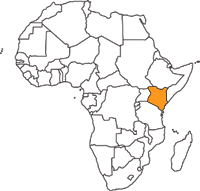
Protected Areas in Kenya
Responsibility for environmental management lies with the National Environment Secretariat (NES), within the Ministry of Environment and Natural Resources. This Secretariat, which was established in 1974, lays down the country's general policy on environmental management and plays a key role in environmental impact assessments.
In 1989, an amendment to the Wildlife Act created the parastatal Kenya Wildlife Service (KWS). The principal goals of KWS, which came into existence on 15 January 1991, are: to conserve natural environments and their flora and fauna; to use the wildlife resources sustainably for the economic development of the nation and for the benefit of people living in wildlife areas; and to protect people and property from injury or damage caused by wildlife. Responsibilities of this corporate body include, inter alia: the formulation of policies concerning conservation, use and management of flora and fauna; advising the government on the establishment of national parks, national reserves and other protected wildlife sanctuaries; preparing and implementing management plans for protected areas; conducting and coordinating research activities for wildlife conservation and management; and administering and coordinating international wildlife protocols, conventions and treaties.
National reserves are vested in the ownership of the local councils and are administered by district councils, with the exception of Shimba Hills which is managed directly by KWS.
Designations:
- National Park: Prohibited activities in such areas include: hunting; being in possession of any weapon or trap; cutting, injuring or setting fire to any vegetation; collecting or attempting to collect any honey or beeswax; the wilful damage or removal of any object of geological, prehistoric, archaeological,historic, marine, or scientific interest; the introduction of any animal or vegetation; the clearing or cultivating of any land; deliberately disturbing animals; and the catching or attempting to catch any fish without prior authorisation.
- Marine National Park: The flora and fauna is totally protected in such areas. Passage and anchorage of boats is permitted but a free permit must be obtained for the period required. Certain other activities such as swimming, water skiing and sailing are allowed.
- National Reserve: Land uses other than nature conservation may be specifically allowed; the conditions controlling such uses are included in regulations agreed to by the authority at the time of gazettement. Exploitation in the form of seasonal water rights and grazing by pastoralists is usually permitted in such areas.
Sources: World Database on Protected Areas, Kenya Wildlife Service (KWS)
|
|