|
Parks, Reserves, and Other Protected Areas in |
|
Malaysia
|
|
|
|
 |
Regions
|
| Protected Areas in Malaysia
Department of Wildlife and National Parks
The Department of Wildlife and National Parks (DWNP) is responsible for the management of national parks and wildlife reserves in Peninsular Malaysia. The management of these areas is focused on the planning and implementation of various activities which contribute to the long-term conservation of protected areas while mitigating/reducing conflicts between human and the environment. The development of protected areas was done sustainably to ensure optimum benefit to human and prosperity to the environment for the present and future generation.
Source: Department of Wildlife and National Parks, Peninsular Malaysia
|
|
|
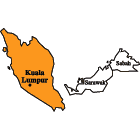 |
Peninsular Malaysia
National Parks
- Taman Negara
- Taman Negara Pulau Pinang
- Tasek Bera
Wildlife Reserves
- Chior
- Sungkai
- Batu Gajah
- Bukit Fraser
- Pahang Tua
- Krau
- Port Dickson
- Bukit Nanas
- Selangor Golf Club
- Klang Gate
- Bukit Sungai Puteh
- Bukit Kutu
- Bukit Faser
- Bukit Melawati
- Templer Park
- Sungai Dusun
- Segamat
- Endau-Kota Tinggi (East)
- Endau-Kota Tinggi (West)
- Endau-Kluang
- Wang Pinang
- Terrapin Reserves
|
|
 |
Sabah
Parks
Protection Forest Reserves
- Bald Hill
- Balembangan
- Bengkoka
- Bidu-Bidu
- Binsuluk
- Botitian
- Bkt. Taviu
- Bkt. Kuamas
- Danum Valley
- Gemok Hill
- Gomantong
- Gn. Lumaku (upper)
- Gn. Lumaku (lower)
- Kelawat
- Klias
- Lamag
- Leila
- Limau-Limauan
- Lipaso
- Maliau Basin
- Mandamai
- Mt. Andrassy
- Mt. Cochrane
- Mt. Conner
- Mt. Hatton
- Mt. Pock
- Mt. Walker
- Mt. Wullersdorf
- Pababag Island
- Quion Hill
- Segarong
- Selangan Is.
- Silabukan
- Sosopodon
- Sg. Serudong
- Tambalugu
- Tanjung Nagas
- Tawai
- Tenompok
- Timbun Mata
- Tinagat
- Ulu Kalumpang
- Ulu Telupid
Domestic Forest Reserves
- Jembongan
- Kawang
- Labuan
- Lema'as
- Matunggong
- Tagaroh
- Tamparuli
- Tajong
- Tatahan
- Tamalang
Amenity Forest Reserves
- Babanga
- Baradaya
- Gum Gum
- Kg. Hindian
- Membalua
- Milli Nonum
- Nabahan
- Padas Damit
- Pulau Berhala
- Sibuga
- Sook Plain
- Ulu Kukut
Virgin Jungle Reserves
- Agathis
- Batumapun (mangrove)
- Batu Timbang
- Bod Tai
- Bohihan, Maganting, Silumpat & Tabawan Islands
- Brantian-Tatulit
- Crocker Range
- Dagat
- Garinono
- Gomantong
- Imbok
- Kabili-Sepilok
- Karakit
- Keruak
- Kretam
- Kawang Gibong
- Kalumpang
- Labuk Road
- Kitabu
- Lajong
- Loro
- Lungmanis
- Madai-Baturong
- Malawaring
- Maligan
- Malubuk
- Mamahat
- Materis
- Mengalong
- Merisuli
- Milian-Labau
- Nurod Urod
- Pangi
- Pin-Supu
- Pulau Batik
- Pulau Sakar
- Rafflesia
- Sepagaya
- Sepilok (mangrove)
- Sg. Basio
- Sg. Imbak
- Sg. Kapur
- Sg. Lokan
- Sg. Paitan
- Sg. Sansiang
- Sg. Sapi
- Sg. Simpang
- Sg. Siliawan
- Sem Kerangas
- Siaunggau & Mesapol
- Silabukan
- Tabin (in Tabin Wildlife Reserve)
- Teak Plantation
- Ulu Sapa Payau
- Ulu Sg. Napagon
- Umas Umas
Wildlife Reserves
Conservation Areas
- Maliau Basin
- Danum Valley
|
Sabah Forest Department
Protection Forest Reserves are strictly protected. The total area of forests under this class is 342,216 ha, about 9.5% of the total forest reserve area (collectively known as the Permanent Forest Estate) and about 4.6% of the land area of Sabah. They are conserved primarily for environmental protection and biodiversity conservation. They are protected by law from any form of land conversion or timber exploitation. After the establishment of the PFE in 1984, a total of 44 Protection FRs were established, the last being Maliau Basin Forest Reserve in 1997.
Domestic Forest Reserves were established mainly to provide forest areas for natives living nearby to hunt, fish and take minor forest produce for their own domestic use, subject to permits. The total area of forests under this class is 7,355 ha. Forests under this class cover only a tiny fraction (0.2%) of the total forest reserve area (the Permanent Forest Reserve, PFE). Domestic FRs have yet to be fully developed for their intended purpose.
Amenity Forest Reserves were established mainly to provide recreational opportunities for the general public. The total area of forests under this class is 20,767 ha. Forests under this class occupy only a tiny fraction (0.6%) of the total forest reserve area (the Permanent Forest Reserve, PFE). Amenity FRs have yet to be fully developed for their intended purpose.
Virgin Jungle Reserves are intended for research and biodiversity conservation. At present, there some 50 VJRs throughout Sabah covering a total of 90,386 ha, about 2.5% of the total forest reserve area (referred to as the Permanent Forest Estate or PFE). Their size ranges from 3 ha to over 18,000 ha. Most of them are situated in the East Coast, on the Kinabatangan Floodplain, and in the southeast, in the Lahad Datu and Tawau regions.
Wildlife Reserves are strictly protected. The total area of forests under this class is 132,653 ha. They are conserved primarily for the preservation of wildlife and wildlife habitat. They are managed by the Sabah Wildlife Department.
Source: Conservation Areas Information and Monitoring System - CAIMS (for the Forest Reserves in Sabah)
|
|
|
 |
Sarawak
National Parks
- Bako (www)
- Gunung Mulu (www)
- Niah (www)
- Lambir Hills (www)
- Similajau (www)
- Gunung Gading (www)
- Kubah (www)
- Batang Ai (www)
- Loagan Bunut (www)
- Tanjung Datu (www)
- Talang Satang (www)
- Bukit Tiban (www)
- Maludam (www)
- Rajang Mangroves (www)
- Gunung Buda (www)
Nature Reserves
- Wind Cave (www)
- Sama Jaya (www)
- Semenggoh (www)
- Bukit Sembiling
- Bukit Hitam
Wildlife Sanctuaries
- Samunsam (www)
- Lanjak-Entimau (www)
- Pulau Tukong Ara-Banun (www)
- Sibuti
|
Sarawak Forest Department
Totally Protected Area (TPA) in Sarawak refers to forest lands so designated and established under the provisions of the National Parks Ordinance (1956) and Wild Life Protection Ordinance (1958). These forest lands are managed to generate sustainable benefits for the society. Their roles include:
- conservation and protection of wildlife and their habitat;
- preservation of specific natural geological or physiographic features, landscape and site, of special interest for archaeological, recreational, educational or conservation purposes, on land and in areas beneath the territorial waters of the State;
- facilitating study and research on the biodiversity of the State;
- preservation and protection of the natural scenic beauty, and the historical sites and historical monuments on land and in the territorial waters of the State; and
- affording opportunities for public appreciation, enjoyment, interest and education of the natural scenic beauty, wildlife habitat, flora and fauna, geological and physiographic features and landscape, historical sites and historical monuments of the State.
The designated TPA system covers about 1 million hectares of forests, or 8% of Sarawak's total area. Inhabitants of Sarawak are prohibited from hunting and fishing and from taking any form of forest produce in the TPA.
These forest lands are classified as National Parks, Wildlife Sanctuaries, Wildlife Rehabilitation Centres, Nature Reserves and Marine Parks.
There are three categories of TPA's in Sarawak:
- National Parks
- Wildlife Sanctuaries
- Nature Reserves
National Parks are open to the public for recreation, but the Wildlife Sanctuaries have limited public access and are strictly for conservation and research. Nature Reserves have the same functions as National Parks except that they are smaller in size, being less than 1,000 ha.
Source: Sarawak Forest Department
|
|