 |
National Parks
- Kuru Hills
- Lake Mape/Mabesi
- Lake Sonfon
- Loma Mountains
- Outamba-Kilimi
- Western Area
Game Sanctuaries
Game Reserves
- Bagru-Moteva Creeks
- Bumpe Mangrove Swamp
- Kagboro Creek (Yawri Bay)
- Kpaka-Pujehun
- Sewa-Waanje
No or Non - Hunting Forest Reserves
- Kangari Hills
- Loma Mountains
- Sankan Biriwa (Tingi Hills)
- Western Area
Strict Nature Reserves
- Bonthe Mangrove Swamp
- Gola (West) Forest
- Gola North
- Gola North Extension
- Mamunta-Mayoso Sanctuary
- Mogbai (Gola North)
- Port Loko Plains
- Sulima Mangrove Swamp
- Wemago (Gola East)
- Yelibuya Island
Forest Reserves
- Bojeni Hills
- Dodo Hills
- Fabina
- Farangbaia
- Forest Reserve (Name unknown1)
- Forest Reserve (Name unknown2)
- Forest Reserve (Name unknown3)
- Forest Reserve (Name unknown4)
- Forest Reserve (Name unknown5)
- Forest Reserve (Name unknown6)
- Forest Reserve (Name unknown7)
- Forest Reserve (Name unknown8)
- Freetown Water Works
- Gboi Hills
- Gola East
- Gola West
- Golamo South
- Gori Hills
- John Obey
- Kambui Hills and Extensions
- Kambui North
- Kambui South
- Kandesuri
- Kasewe
- Kent Extension
- Kuru Hills
- Lalay
- Leicester Peak
- Lhei Hills
- Malal Hills
- Matete
- Moku Hill
- Moyamba Hills
- Nimini South
- No. 2 River Extension
- Occra Hills
- Peninsula
- Port Loko
- Singamba
- Sipende
- Tabe
- Tama
- Tobi
- Tonkoli
- Wara Wara Hills
- Waterloo
Wetlands of International Importance (Ramsar)
- Sierra Leone River Estuary
Cloud Forest Sites
- Mount Bintumani
- Sankan Biriwa
|
|
Info
|
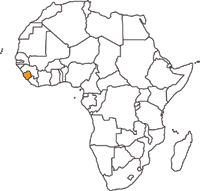
Protected Areas in Sierra Leone
Today, the primary piece of legislation dealing with wildlife conservation is the Wild Life Conservation Act No. 27, 1972, amended 1990. This Act identifies national park, strict nature reserve, game reserve, game sanctuary, controlled hunting area, and non-hunting forest reserve
The Ministry of Agriculture, Natural Resources and Forestry (MANRF) was formed in 1984. Falling under this Ministry is the Forestry Division which is responsible for managing the forest estate, while the Wildlife Conservation Branch within this Division manages the national parks and wildlife sector reserves, and is responsible for the conservation of flora and fauna throughout the country.
Traditionally, forestry has been a neglected sector within this Ministry, with its role in land use and economic development being totally overlooked. Consequently, there has been a lack of development and operational resources, including field equipment, vehicles, qualified personnel and funds to enable the Forestry Division to function effectively insofar as the conservation and management of national forests are concerned.
Wildlife, parks and environmental management are also badly neglected and the Wildlife Conservation Branch needs restructuring and strengthening.
The greatest threat to the native flora and fauna is environmental degradation through uncontrolled forest clearance and agricultural expansion; in 200 years the country has lost over 97% of its primary forest. All forest reserves, including the four non-hunting reserves, are intensively hunted and are experiencing agricultural encroachment.
Sources: World database on Protected Areas; UNEP-WCMC
|
|