Parco Naturale Regionale Costa Otranto - S.Maria Leuca - Bosco Tricase
www.parcootrantoleuca.itProtected Area
Identity Card
- Land Surface Area: 3'227.00 ha
- Regions: Puglia
- Provinces: Lecce
- Municipalities: Alessano, Andrano, Castrignano del Capo, Castro, Corsano, Diso, Gagliano del Capo, Ortelle, Otranto, Santa Cesarea Terme, Tiggiano, Tricase
- Establishment Measures: L.R. 30 26/10/2006
- PA Official List: EUAP1192
- Park Authority: Consorzio di Gestione del Parco Regionale Costa Otranto-Santa Maria di Leuca e Bosco di Tricase
The Park
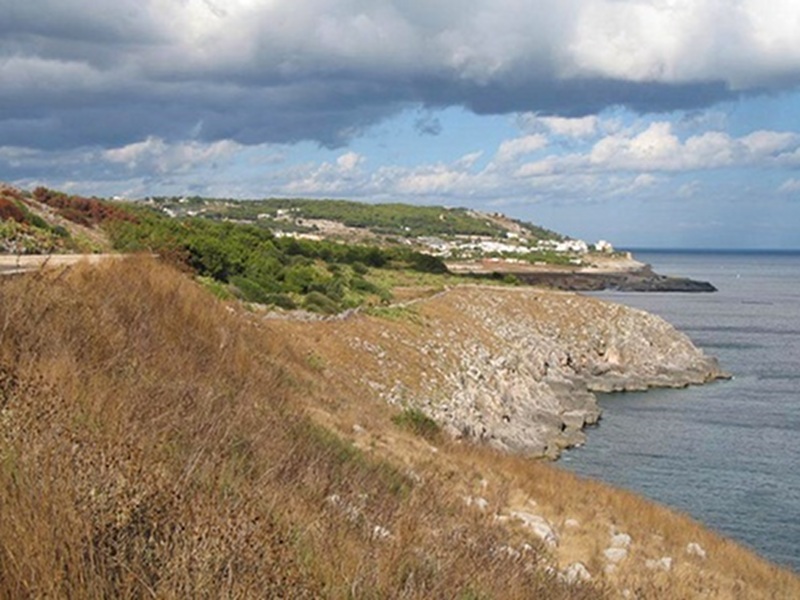
Costa Otranto - Santa Maria di Leuca e Bosco di Tricase Regional Nature Park is a regional park in Puglia established with the Regional Law n. 30 of the 26th October 2006.
Since the 29th of July 2008 the Park has a management association with its head office in the Andrano castle.
The Park was established as a consequence of the will to safeguard a unique natural heritage of very high scientific and cultural value, and to enhance the territory according to an environment-friendly development model that guarantees the biodiversity safeguard while fostering the reference community's economy. Among the goals that the regional law 30/2006 ascribes to the establishment of the Park there is also the streamlining of the administrative procedures and the promotion of the activities by involving the local communities.
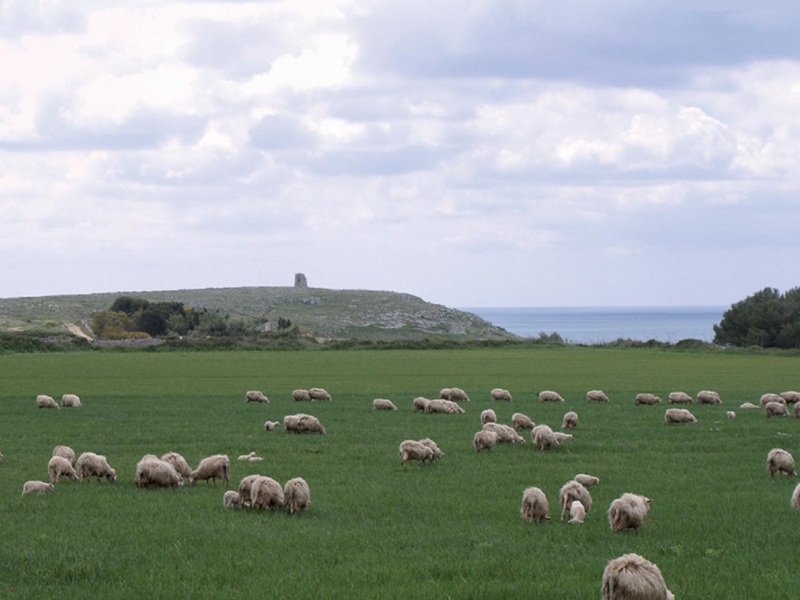
The Park includes some Sites of Community Importance in accordance with the Habitats directive 92/43/EC: Costa Otranto – Santa Maria di Leuca (IT9150002), Boschetto di Tricase (IT9150005) and Parco delle querce di Castro (IT9150019). It covers a surface of 3,227 hectares, and with an area of about 57 km along Salento's eastern coast it represents the biggest among the regional parks established in the province of Lecce. Twelve municipalities belong to it: Alessano, Andrano, Castrignano del Capo, Castro, Corsano, Diso, Gagliano del Capo, Ortelle,Otranto, Santa Cesarea Terme, Tiggiano and Tricase.
The Protected Area
The Park's territory develops along a large SCI (Site of Community Importance) and includes or is connected with other 4 sites of particular conservation significance, whose perimeter as a SCI has been evaluated in accordance with the Habitats Directive 92/43 EEC.
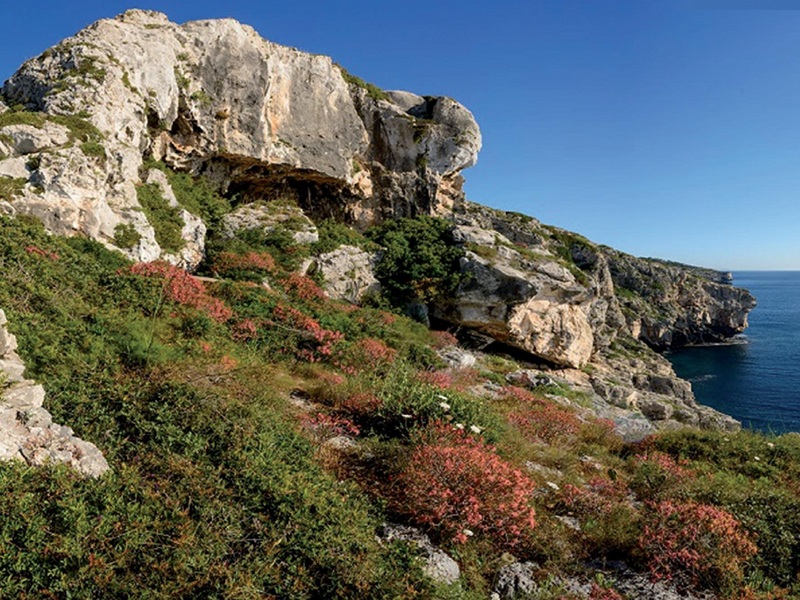
Most of the Protected Area is situated along the coastal perimeter and it is characterized by several environments such as holm oak forests, pinewoods, areas with kermes oaks and other sclerophylls, garrigues, old pastures, rocks and cliffs overlooking the sea.
Biodiversity
Flora
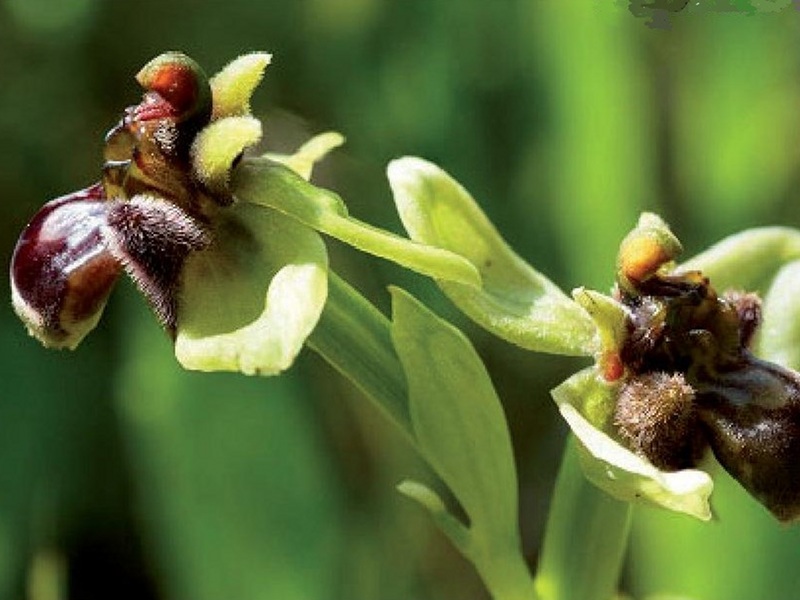
The flora is rich in endemic species included in the national "red list", and in trans-adriatic and trans-ionian species enhancing the phytogeographic value of the coast.
There are also remarkable botanical rarities such as the Centaurea leucadea, the Aurinia leucadea, the campanula versicolor, the Ephedra campylopoda (it grows only in this part of Italy), and the very rare Vicia giacominiana, an endemism with well visible populations in the area of Porto Badisco.
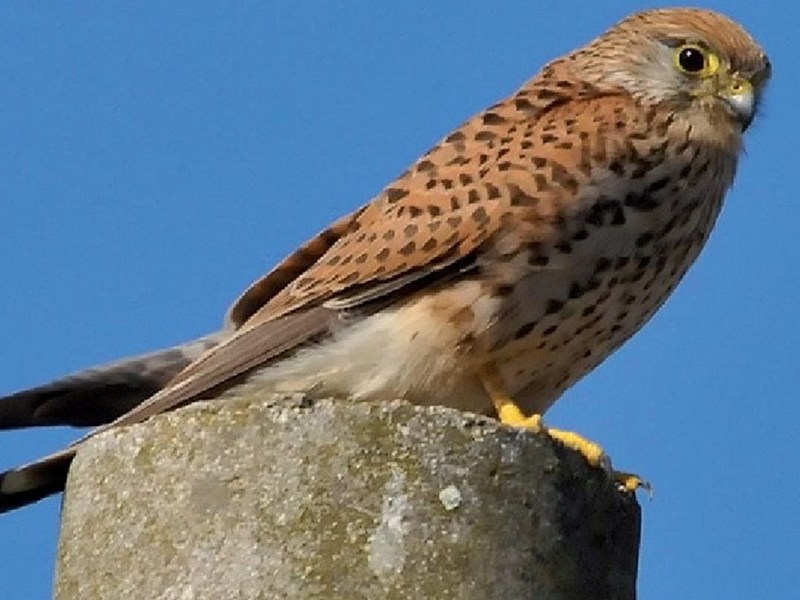
Fauna
The richness in karstic and erosion phenomena mostly shows itself in the many coastal caves - sometimes semi-submerged - that represent real sanctuaries with geomorphological values and animal rarities.
As far as the fauna is concerned, it is remarkable that in this area the regional presence of Europe's rarest mammal was observed for the last time: the Mediterranean monk seal (Monachus monachus).
Geological structure
The Park's surface is characterized by a very particular stratigraphic architecture due to the fact that several carbonate systems, that developed between the late cretaceous and the quaternary, are placed laterally and inserted one in the other. These layers, of which some stretches remained unchanged, have notable thicknesses and form unbelievable passages that are a testimony to the complex events of the long geological evolution occurred over the last 65 million years.
Habitat
The Park's area includes significant environments and biocoenosis of remarkable interest for the conservation of the landscape and the biodiversity in Puglia. The "Costa Otranto Leuca e Bosco di Tricase Regional Nature Park" extends over a surface of about 3,200 hectares, and it includes three Sites of Community Importance (IT9150002 Costa Otranto Leuca, IT9150005 Boschetto di Tricase and IT9150019 Parco delle Querce di Castro). In its territory there are 5 Habitats of community interest and 1 Habitat of priority interest.