Parco Nazionale dell'Appennino Lucano
Val d'Agri - Lagonegrese
www.parcoappenninolucano.itFrom prehistory to the Hellenistic-Lucanian era
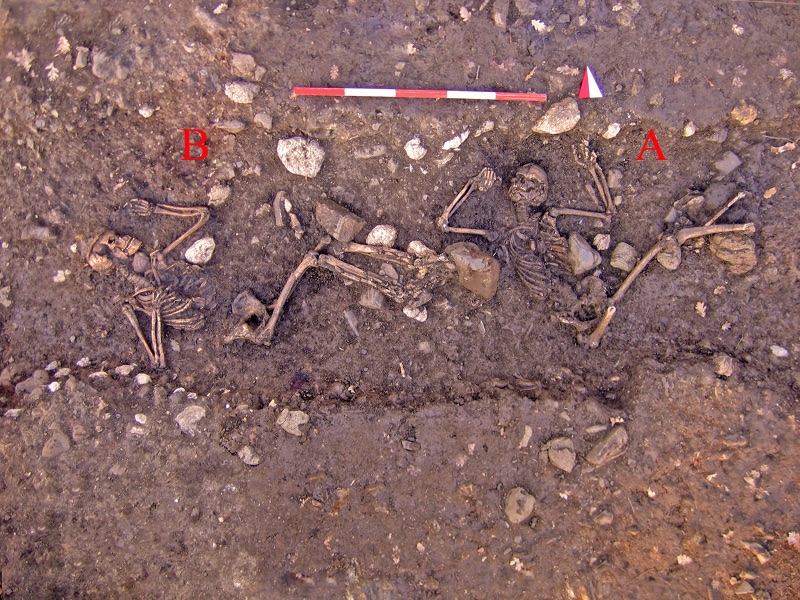
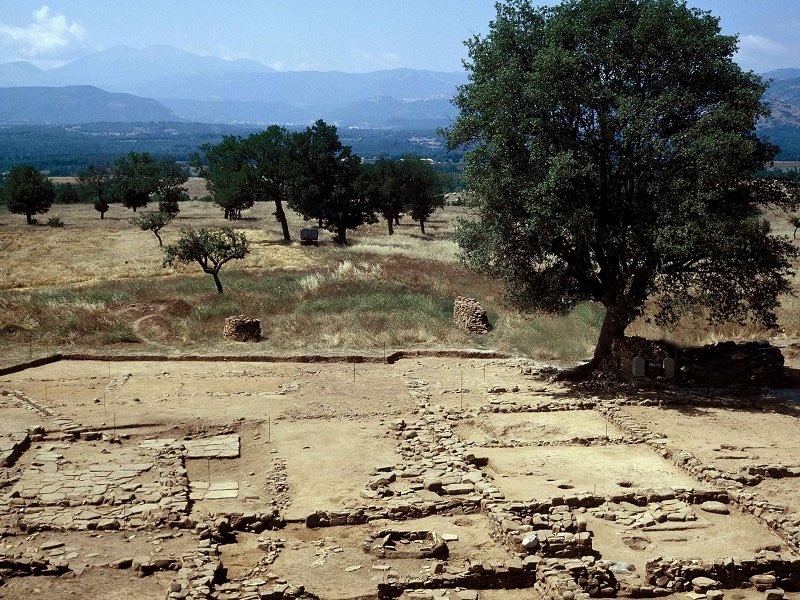
During the Pleistocene (ranging from 2,588,000 years ago to around 11,700 years ago), the physical geography of the valley was totally different from how we see it today: the entire Agri plain was covered by a natural lake basin, and a diverse fauna must have lived along the banks, including elephas antiquus, whose remains, dating back some 500,000 years ago (Lower Palaeolithic), found in the locality of San Giuliano in Grumento Nova, are still preserved in the National Archaeological Museum of the Alta Val d'Agri. People who inhabited the area also lived mainly by hunting and gathering.
© 2024 - Ente Parco Nazionale dell'Appennino Lucano - Val d'Agri - Lagonegrese