Riserva Naturale Monte Alpe
www.ersaf.lombardia.it/biodiversita-e-aree-protette/riserve-naturali/riserva-naturale-monte-alpe/Points of Interest
Interventions
On 27th February 1990 under the S.S. road no. 461 of Penice, in location
Carpaneto, a fire burst out. Because of the strong wind, the fire
rapidly extended and reached during the night most of the artificial
conifer plantations of the nature reserve.
The day after, also thanks to the water thrown from the helicopters of the regional authorities, the fire was extinguished.
Because
of the wind and of the features of the superficial soil, whose initial
structure was very thick and which had considerable quantities of dry
material inside it, the fire burnt both the tree trunks and foliage.
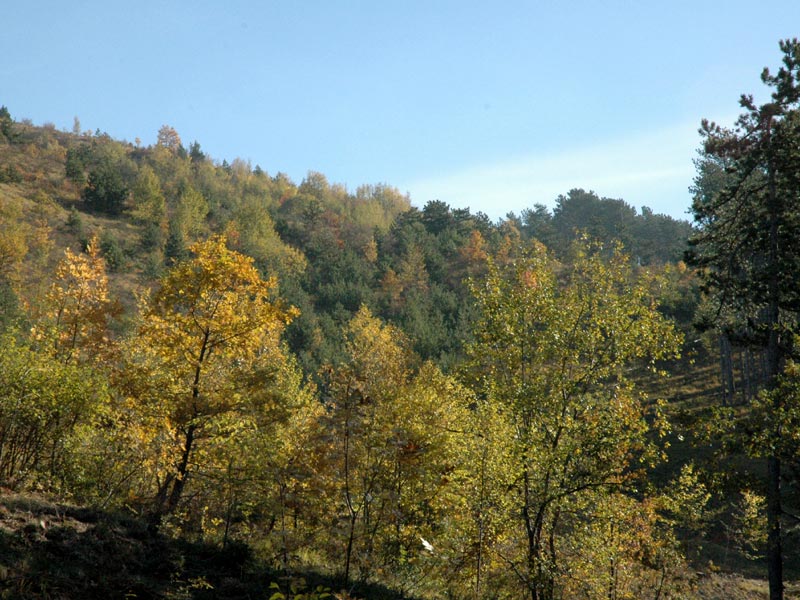
The
fire devastated an estimated area of 141 hectares, which was
exclusively covered by a contemporary and monospecific population of
Austrian Pines about 60 years old.
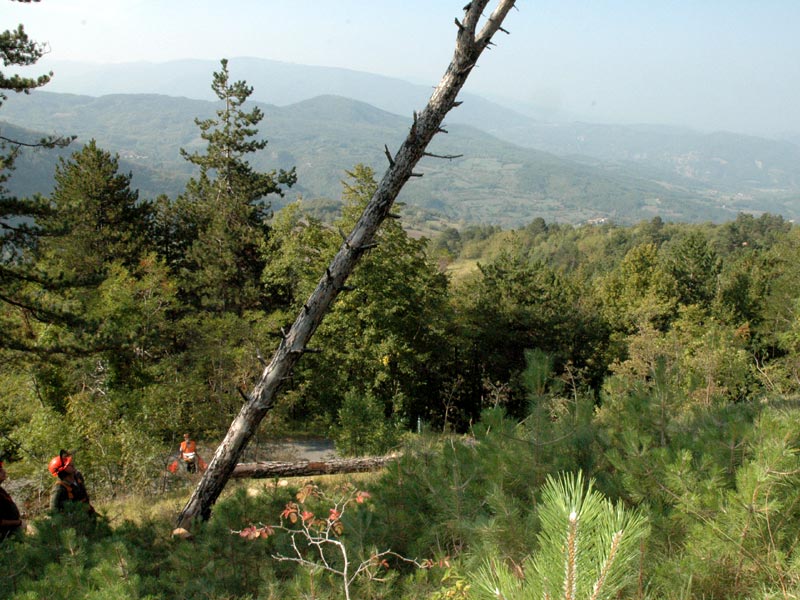
The most damaged woods have been subject to clear cutting,
since they have been irremediably jeopardized by the fire and by the
following massive attacks by the Bark Beetle (Ips sexdentatus).
The fire has deeply changed the biological asset of the reserve,
leading to considerable damages, but at the same time freeing dynamic
forces tending to increase the biologic variety, and therefore led to a
greater ecological stability.
Immediately after the fire, Azienda Regionale delle Foreste carried
out urgent interventions in order to limit phenomena of hydrogeological
instability and environmental deterioration. Herbaceous plants were
seeded in the most damaged areas; burnt trees were removed only from
partially damaged areas.
Since October 1991, the
interventions regarding the clear cutting of the burnt and irremediably
damaged wood have began. The involved area extended for a total of
about 58.5 hectares.
Afterwards, the reforestation was carried out
on the surfaces subject to clear cut by using autochthonous forest
species, to recover an ecologically steady wood with a good economic
value.
The number of seedlings used per hectare varied from 1,500 to 2,500
units, according to the already established presence of natural renewal.
The main species which have been used are the following ones: Quercus
cerris, Quercus petraea, Quercus robur, Carpinus betulus, Ostrya
carpinifolia, Acer campestre, Acer pseudoplatanus, Acer platanoides,
Fraxinus ornus, Fraxinus excelsior, Prunus avium, Prunus padus, Ulmus
minor, Laburnum anagyroides, Malus sylvestris, Fagus sylvatica, Sorbus
domestica, Alnus glutinosa, Abies alba, Pinus sylvestris; and the
following shrubs: Crataegus monogyna, Prunus spinosa, Pyrus communis,
Cornus sanguinea, Corylus avellana, Sambucus nigra, Rosa canina,
Viburnum lantana, Ligustrum vulgare, Amelanchier ovalis.